分类:三角形SAS(边角边)全等判定定理
定义和含义
三角形SAS(边角边)全等判定定理,指的是,两个三角形的两条边对应相等,同时这两条边的夹角也相等,则这两个三角形全等[1]。
(图片来源于《小学数学这样学》[1])
层次标注
在这里,它属于第二层知识,即学科概念。
证明过程
它的证明依靠着直线存在和唯一性定理。
以下是摘自《小学数学这样学》的证明内容[1]:
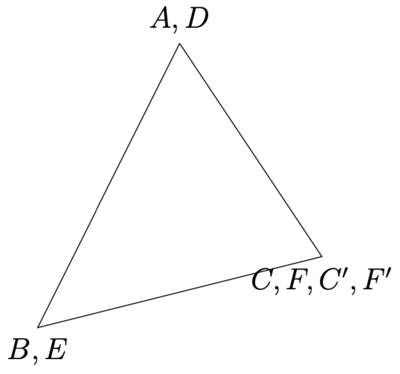
证明:如图所示, [math]\displaystyle{ \triangle A B C }[/math] 和 [math]\displaystyle{ \triangle D E F }[/math] 中 [math]\displaystyle{ A B=D E }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ A C=D F }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \angle B A C=\angle E D F }[/math] ,我们来证明两个三角形全等。
取两个三角形 [math]\displaystyle{ \triangle A B C }[/math] 和 [math]\displaystyle{ \triangle D E F }[/math] 中对应相等的两条边中的一条, 例如, [math]\displaystyle{ A B }[/math] 和 [math]\displaystyle{ D E }[/math] , 先重叠起来。由于夹角相同, 因此, 另一条边的方向也相应重合。现在注意 [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math] 点和 [math]\displaystyle{ E }[/math] 点已经重合, [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math] 点和 [math]\displaystyle{ D }[/math] 点也重合。我们在另一条边所在的射线方向上, 选取点 [math]\displaystyle{ C^{\prime} }[/math] 和 [math]\displaystyle{ F^{\prime} }[/math] 使得其长度 [math]\displaystyle{ A C^{\prime}=D F^{\prime}=A C=D F }[/math] ,由于 [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math] 、 [math]\displaystyle{ D }[/math] 重合,在射线方向上,给定长度和点一一对应, 因此, [math]\displaystyle{ C^{\prime} }[/math] 和 [math]\displaystyle{ F^{\prime} }[/math] 点也重合, 而且刚好就是 [math]\displaystyle{ C }[/math] 和 [math]\displaystyle{ F }[/math] 点。由于过给定两点有且只有一条直线 (或者说只能连一条线段,也就是引用了直线存在和唯一性定理), 因此, [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math]、 [math]\displaystyle{ E }[/math] 重合, [math]\displaystyle{ C }[/math]、 [math]\displaystyle{ F }[/math] 重合, 因此 [math]\displaystyle{ B C }[/math] 也就是 [math]\displaystyle{ E F }[/math] 。因此,两个三角形完全重合。完全重合的三角形的各个角度和各条边肯定都对应相等。因此,这两个三角形是全等三角形。
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 吴金闪,《小数数学这样学》,浙江人民出版社,2023, http://www.systemsci.org/jinshanw/books
本分类目前不含有任何页面或媒体文件。