Rust
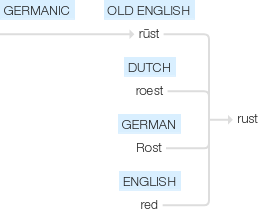
Old English rūst, of Germanic origin; related to Dutch roest, German Rost, also to red.
wiktionary
From Middle English rust, rost, roust, from Old English rust, rūst(“rust”), from Proto-West Germanic *rust, from Proto-Germanic *rustaz(“rust”), from Proto-Indo-European *rudʰso-(“red”), from Proto-Indo-European *h₁rewdʰ-(“red”).
Cognate with Scots roust(“rust”), Saterland Frisian rust(“rust”), West Frisian roast(“rust”), Dutch roest(“rust”), German Rost(“rust”), Danish rust(“rust”), Swedish rost(“rust”), Norwegian rust, ryst(“rust”). Related to red.
From Middle English rusten, from the noun (see above).
etymonline
rust (n.)
"red oxide of iron, red coating which forms on the surface of iron exposed to the air," Old English rust "rust," in late Old English also figurative, "anything tending to spiritual corrosion, a moral canker," related to rudu "redness," from Proto-Germanic *rusta- (source also of Frisian rust, Old High German and German rost, Middle Dutch ro(e)st), from PIE *reudh-s-to- (source also of Lithuanian rustas "brownish," rūdėti "to rust;" Latin robigo, Old Church Slavonic ruzda "rust"), from suffixed form of root *reudh- "red, ruddy."
As a morbid condition of plants caused by fungal growth, from mid-14c. U.S. colloquial rust-bucket for "old car or boat" is by 1945. Rust Belt "decayed urban industrial areas of mid-central U.S." (1984) was popularized in, if not coined by, Walter Mondale's presidential campaign.
rust (v.)
early 13c., rusten, of metals, "become rusty, gather rust," from rust (n.). The transitive sense of "cause to rust" is from 1590s. The figurative sense in reference to anything deteriorating or spoiling from disuse or idleness is by early 14c. Related: Rusted; rusting.