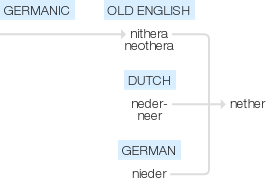
Nether
Old English nithera, neothera, of Germanic origin; related to Dutch neder- (found in compounds), neer, and German nieder, from an Indo-European root meaning ‘down’.
wiktionary
From Middle English nether, nethere, nithere, from Old English niþera(“lower, under, lowest”, adjective), from niþer, niþor(“below, beneath, down, downwards, lower, in an inferior position”, adverb), from Proto-West Germanic[Term?], from Proto-Germanic *niþer, *niþra(“down”), from Proto-Indo-European *ni-, *nei-(“in, down”). Cognates include Dutch neder, German nieder, Luxembourgish nidder, Danish, Norwegian and Swedish ned, Faroese and Icelandic niður.
Alteration of earlier nither, from Middle English nitheren, from Old English niþerian(“to depress, abase, bring low, humiliate, oppress, accuse, condemn”), from niþer(“below, beneath, down, downwards, lower, in an inferior position”). See above.
etymonline
nether (adj.)
Old English niþera, neoþera "down, downwards, lower, below, beneath," from Proto-Germanic *nitheraz (source also of Old Saxon nithar, Old Norse niðr, which contributed to the English word, Old Frisian nither, Dutch neder, German nieder), from comparative of PIE *ni- "down, below" (source also of Sanskrit ni "down," nitaram "downward," Greek neiothen "from below," Old Church Slavonic nizŭ "low, down").
Also an adverb in Old English and Middle English. It has been replaced in most senses by lower (adj.). Of countries, "situated on lower ground" (late 14c.). In Middle English (and after) used also of body parts.
Absolon hath kist hir nether eye. [Chaucer, "Miller's Tale"]