Navy
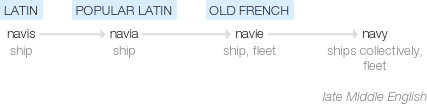
late Middle English (in the sense ‘ships collectively, fleet’): from Old French navie ‘ship, fleet’, from popular Latin navia ‘ship’, from Latin navis ‘ship’.
wiktionary
From Middle English nave, navye, from Anglo-Norman, Old French navie, from Latin nāvigia < nāvigium, from Latin nāvigō, nāvis(“boat”), from Proto-Indo-European *néh₂us. Compare Ancient Greek ναῦς(naûs, “ship”), Persian ناو (nâv, “boat, warship”), Sanskrit नाव(nāva, “ship”), Old English nōwend(“mariner, sailor”).
etymonline
navy (n.)
mid-14c., navie, "fleet of ships," especially for purposes of war, from Old French navie "fleet; ship," from Latin navigia, plural of navigium "vessel, boat," from navis "ship," from PIE root *nau- "boat."
Meaning "a nation's collective, organized sea power" is from 1530s. The Old English words were sciphere (usually of Viking invaders) and scipfierd (usually of the home defenses). Navy blue was the color of the British naval uniform. Navy bean attested from 1856, so called because they were grown to be used by the Navy. Navy-yard "government dockyard," in the U.S. "a dockyard where government ships are built or repaired" is by 1842.