Hedge
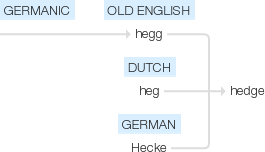
Old English hegg, of Germanic origin; related to Dutch heg and German Hecke .
wiktionary
From Middle English hegge, from Old English heċġ, from Proto-West Germanic *haggju, from Proto-Germanic *hagjō, from Proto-Indo-European *kagʰyóm. Cognate with Dutch heg, German Hecke. Doublet of quay. More at haw.
From Middle English heggen, from the noun (see above).
etymonline
hedge (n.)
Old English hecg "hedge," originally any fence, living or artificial, from West Germanic *hagjo (source also of Middle Dutch hegge, Dutch heg, Old High German hegga, German Hecke "hedge"), from a verb *hagjanan, from PIE root *kagh- "to catch, seize; wickerwork, fence" (source also of Latin caulae "a sheepfold, enclosure," Gaulish caio "circumvallation," Welsh cae "fence, hedge"). Related to Old English haga "enclosure, hedge" (see haw (n.)).
Figurative sense of "boundary, barrier" is from mid-14c. As hedges were "often used by vagabonds as places of shelter or resort" [Century Dictionary], the word, compounded, "notes something mean, vile, of the lowest class" [Johnson], from contemptuous attributive sense of "plying one's trade under a hedge" (hedge-priest, hedge-lawyer, hedge-wench, etc.), a usage attested from 1530s. The noun in the betting sense is from 1736 (see hedge (v.)).
hedge (v.)
late 14c., "make a hedge," also "surround with a barricade or palisade;" from hedge (n.). The intransitive sense of "dodge, evade, avoid committing oneself" is first recorded 1590s, on the notion of hiding as if in a hedge. That of "insure oneself against loss," as in a bet, by playing something on the other side is from 1670s, originally with in; probably from an earlier use of hedge in meaning "secure (a debt) by including it in a larger one which has better security" (1610s). Related: Hedged; hedging. The noun in the wagering sense is from 1736.