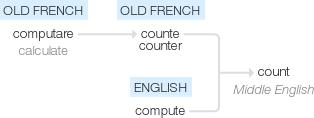
Count
Middle English (as a noun): from Old French counte (noun), counter (verb), from the verb computare ‘calculate’ (see compute).
wiktionary
From Middle English counten, borrowed from Anglo-Norman conter, from Old French conter(“add up; tell a story”), from Latin computare, present active infinitive of computō(“I compute”). Displaced native Middle English tellen(“to count”) (from Old English tellan) and Middle English rimen(“to count, enumerate”) (from Old English rīman). Doublet of compute.
From Middle English counte, from Anglo-Norman conte and Old French comte(“count”), from Latin comes(“ companion”) (more specifically derived from its accusative form comitem) in the sense of "noble fighting alongside the king". Doublet of comes and comte.
etymonline
count (v.)
late 14c., "to enumerate, assign numerals to successively and in order; repeat the numerals in order," also "to reckon among, include," from Old French conter "to count, add up," also "tell a story," from Latin computare "to count, sum up, reckon together," from com "with, together" (see com-) + putare "to reckon," originally "to prune," from PIE root *pau- (2) "to cut, strike, stamp."
Intransitive sense "be of value or worth" is from 1857. Related: Counted; counting. Modern French differentiates compter "to count" and conter "to tell," but they are cognates. To count on "rely or depend upon" is from 1640s. To count against (transitive) "to be to the disadvantage of" is by 1888. To count (someone) in "consider (someone) a participant or supporter" is from 1857; count (someone) out in the opposite sense "leave out of consideration" is from 1854.
count (n.1)
title of nobility in some continental nations, corresponding to English earl, c. 1300, from Anglo-French counte "count, earl" (Old French conte), from Latin comitem (nominative comes) "companion, attendant," the Roman term for a provincial governor, from com "with" (see com-) + stem of ire "to go" (from PIE root *ei- "to go"). The term was used in Anglo-French to render Old English eorl, but the word was never truly naturalized and mainly was used with reference to foreign titles.
In ancient Rome and the Roman empire, [a comes was] a companion of or attendant upon a great person; hence, the title of an adjutant to a proconsul or the like, afterward specifically of the immediate personal counselors of the emperor, and finally of many high officers, the most important of whom were the prototypes of the medieval counts. [Century Dictionary]
count (n.2)
early 14c., "a counting, a calculation," also "an account of money or property;" late 15c., "the total number, the total counted," from Anglo-French counte, Old French conte "a count, a reckoning, calculations," from conter "to count, add up," from Latin computare "to count, sum up, reckon together" (see compute).
Meaning "estimation, esteem, consideration" is from late 15c. In law, "each charge in an indictment," from 1580s. In boxing, "the counting by the referee of the 10 seconds allowed a fallen fighter to get up again," by 1902. In baseball and softball, "the number of strikes and balls thrown to a batter in a turn at the plate," by 1909.