Christ
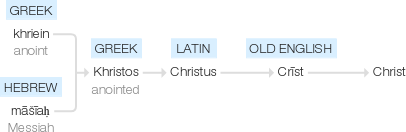
Old English Crīst, from Latin Christus, from Greek Khristos, noun use of an adjective meaning ‘anointed’, from khriein ‘anoint’, translating Hebrew māšīaḥ ‘Messiah’.
wiktionary
From Middle English Crist, from Old English Crist, from Latin Christus, from Ancient Greek Χριστός(Khristós), proper noun use of χριστός(khristós, “[the] anointed [one]”), a calque of Hebrew מָשִׁיחַ (māšīaḥ, “anointed”) (whence English messiah). Doublet of ghee.
etymonline
Christ (n.)
"the Anointed," synonymous with and translating to Greek Hebrew mashiah (see messiah), a title given to Jesus of Nazareth; Old English crist (by 830, perhaps 675), from Latin Christus, from Greek khristos "the anointed," noun use of verbal adjective of khriein "to rub, anoint" (from PIE root *ghrei- "to rub").
In the primitive Church it was a title, and used with the definite article, but from an early period it was used without it and regarded as part of the proper name of Jesus. It was treated as a proper name in Old English, but not regularly capitalized until 17c. Pronunciation with long -i- is result of Irish missionary work in England, 7c.-8c. The ch- form, regular since c. 1500 in English, was rare before. Capitalization of the word begins 14c. but is not fixed until 17c. The Latin term drove out Old English Hæland "healer, savior," as the preferred descriptive term for Jesus.
As an oath or strong exclamation (of surprise, dismay, etc.), attested by 1748. The 17c. mystical sect of the Familists edged it toward a verb with Christed "made one with Christ." Christ-child "Jesus as a baby" (1842) translates German Christkind.