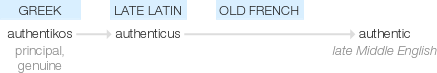
Authentic
late Middle English: via Old French from late Latin authenticus, from Greek authentikos ‘principal, genuine’.
wiktionary
From Middle English authentik, from Old French autentique, from Latin authenticus, from Ancient Greek αὐθεντικός(authentikós, “principal, genuine”), from Ancient Greek αὐθέντης(authéntēs, “lord, master”).
etymonline
authentic (adj.)
mid-14c., autentik, "authoritative, duly authorized" (a sense now obsolete), from Old French autentique "authentic; canonical" (13c., Modern French authentique) and directly from Medieval Latin authenticus, from Greek authentikos "original, genuine, principal," from authentes "one acting on one's own authority," from autos "self" (see auto-) + hentes "doer, being," from PIE root *sene- (2) "to accomplish, achieve." Sense of "real, entitled to acceptance as factual" is first recorded mid-14c.
Traditionally in modern use, authentic implies that the contents of the thing in question correspond to the facts and are not fictitious (hence "trustworthy, reliable"); while genuine implies that the reputed author is the real one and that we have it as it left the author's hand (hence "unadulterated"); but this is not always maintained: "The distinction which the 18th c. apologists attempted to establish between genuine and authentic ... does not agree well with the etymology of the latter word, and is not now recognized" [OED].