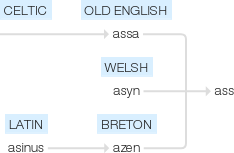
Ass
Old English assa, from a Celtic word related to Welsh asyn, Breton azen, based on Latin asinus .
wiktionary
From Middle English asse, from Old English assa, back-formed from assen(“she-ass”), from Celtic (compare Old Irish asan, Old Cornish asen), from Latin asinus. Replaced Old English esol, from Proto-West Germanic *asil, also a loanword from the same Latin word.
Variant of arse; used chiefly in North America. Ultimately from Middle English ars, ers, from Old English ærs, ears, from Proto-West Germanic *ars, from Proto-Germanic *arsaz (compare Old High German ars (German Arsch), Old Norse ars, Old Frisian ers), from Proto-Indo-European *h₃érsos (compare Ancient Greek ὄρρος(órrhos)).
Contrary to the widespread belief of this being a euphemism, it arose as a pronunciation spelling (of the older form arse still used in the UK, Australia, New Zealand, etc.) that shows the loss of -r- before s increasingly common in all words since the 18th century in both England and its colonies. In the USA, "dropping Rs" (non- rhotic pronunciation) was common in prestige speech until the 1860s, when the American Civil War shifted the country's centers of wealth and political power to areas with fewer cultural connections to the British elite. (See also these similar cases, some of which retained both spellings with different meanings: cuss from curse, gash from garsh, bass(“fish”) from barse, bust from burst, passel from parcel.)
etymonline
ass (n.1)
solid ungulate quadruped beast of burden of the horse kind, but smaller and with long ears and a short mane, native to southwest Asia, Old English assa (Old Northumbrian assal, assald) "he-ass." The English word is cognate with Old Saxon esil, Dutch ezel, Old High German esil, German Esel, Gothic asilus, and, beyond Germanic, Lithuanian asilas, Old Church Slavonic osl, Russian oselŭ, etc. All probably are ultimately from Latin asinus. De Vaan says the form of asinus suggests it was a loan-word into Latin, and adds, "Most IE words for 'ass' are loanwords."
Together with Greek onos it is conjectured to be from a language of Asia Minor (compare Sumerian ansu). The initial vowel of the English word might be by influence of Celtic forms (Irish and Gaelic asal), from Old Celtic *as(s)in "donkey." In Romanic tongues the Latin word has become Italian asino, Spanish asno, Old French asne, French âne.
In familiar use, the name ass is now to a great extent superseded by donkey (in Scotland cuddie); but ass is always used in the language of Scripture, Natural History, proverb, and fable; also, in ordinary use, in Ireland. [OED]
Sure-footed and patient in domestication, since ancient Greek times, in fables and parables, the animal has typified clumsiness and stupidity (hence ass-head, late 15c., etc.). To make an ass of oneself is from "A Midsummer Night's Dream" (1590). Asses' Bridge (c. 1780), from Latin Pons Asinorum, is fifth proposition of first book of Euclid's "Elements." In Middle English, someone uncomprehending or unappreciative would be lik an asse that listeth on a harpe. In 15c., an ass man was a donkey-driver.
For al schal deie and al schal passe, Als wel a Leoun as an asse. [John Gower, "Confessio Amantis," 1393]
ass (n.2)
slang for "backside," first attested 1860 in nautical slang, in popular use from 1930; chiefly U.S.; from dialectal variant pronunciation of arse (q.v.). The loss of -r- before -s- is attested in other words (burst/bust, curse/cuss, horse/hoss, barse/bass, garsh/gash, parcel/passel).
Indirect evidence of the change from arse to ass can be traced to 17c. By 1680s arse was being pronounced to rhyme with "-ass" words, as in "Sodom or the Quintessence of Debauchery": "I would advise you, sir, to make a pass/Once more at Pockenello's loyal arse." It is perhaps as early as Shakespeare's day, if Nick Bottom transformed into a donkey in "A Midsummer Night's Dream" (1594) is the word-play some think it is.
I must to the barber's, mounsieur; for me thinks I am marvellous hairy about the face; and I am such a tender ass, if my hair do but tickle me, I must scratch. [Bottom]
By 1785 polite speakers were avoiding ass in the "donkey" sense.
Meaning "woman regarded as a sexual object" is by early 1940s (piece of ass seems to be implied in 1930s Tijuana Bibles), but the image is older (compare buttock "a common strumpet," 1670s). To have (one's) head up (one's) ass "not know what one is doing" is attested by 1969. Colloquial (one's) ass "one's self, one's person" attested by 1958. To work (one's) ass off "work very much" is by 1946; to laugh (one's) ass off "laugh very much" is by 1972 (implied from 1965). The ('stick it)'''''''up your ass oath is attested by 1953; apparent euphemisms suggest earlier use:
He snoighed up his nose as if th' cheese stunk, eyed me wi an air o contempt fro my shoon to my yed, un deawn ogen fro my yed to my shoon ; un then pushin th' brade un cheese into my hont ogen, he says "Take your vile bread and cheese and stick it up your coat sleeve, and be demmed to you. Do you think I want your paltry grub?" Un then, turnin on his heel, he hurried into th' perk. ["Bobby Shuttle un His Woife Sayroh's Visit to Manchester," 1857]