Argon
来自Big Physics
Safin(讨论 | 贡献)2022年4月28日 (四) 16:25的版本 (建立内容为“Category:etymology == google == [https://www.google.com.hk/search?q=argon+etymology&newwindow=1&hl=en ref] late 19th century: from Greek, neuter of argos ‘…”的新页面)
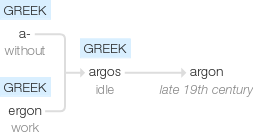
late 19th century: from Greek, neuter of argos ‘idle’, from a- ‘without’ + ergon ‘work’.
wiktionary
From Ancient Greek ἀργόν(argón), neuter of ἀργός(argós, “idle, lazy”), because of its inertness.
etymonline
argon (n.)
chemical element, 1894, Modern Latin, from Greek argon, neuter of argos "lazy, idle, not working the ground, living without labor," from a- "without" (see a- (3)) + ergon "work," from PIE root *werg- "to do." So called by its discoverers, Baron Rayleigh and Sir William Ramsay, for its inert qualities. They described it as "most astonishingly indifferent."