Lock
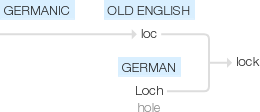
Old English loc, of Germanic origin; related to German Loch ‘hole’.
wiktionary
From Middle English lok, from Old English loc, from Proto-West Germanic *lok, from Proto-Germanic *luką from Proto-Indo-European *lewg-(“to bend; turn”). The verb is from Middle English locken, lokken, louken, from Old English lūcan, Proto-West Germanic *lūkan, from Proto-Germanic *lūkaną. Doublet of luxe.
From Middle English lok, lokke, from Old English locc, from Proto-Germanic *lukkaz, from Proto-Indo-European *lugnó-, from Proto-Indo-European *lewg-(“to bend”).
Cognate with Old Norse lokkr (whence Danish lok), German Locke. It has been theorised that the word may be related to the Gothic verb *𐌻𐌿𐌺𐌰𐌽( *lukan, “to shut”) in its ancient meaning "to curb".
etymonline
lock (n.1)
"means of fastening," Old English loc "bolt, appliance for fastening a door, lid, etc.; barrier, enclosure; bargain, agreement, settlement, conclusion," from Proto-Germanic *lukana-, a verbal root meaning "to close" (source also of Old Frisian lok "enclosure, prison, concealed place," Old Norse lok "fastening, lock," Gothic usluks "opening," Old High German loh "dungeon," German Loch "opening, hole," Dutch luik "shutter, trapdoor").
Ordinary mechanical locks work by means of an internal bolt or bar which slides and catches in an opening made to receive it. "The great diversity of meaning in the Teut. words seems to indicate two or more independent but formally identical substantival formations from the root" [OED]. The Old English sense "barrier, enclosure" led to the specific meaning "barrier on a stream or canal" (c. 1300), and the more specific sense "gate and sluice system on a water channel used as a means of raising and lowering boats" (1570s).
From 1540s as "a fastening together," hence "a grappling in wrestling" (c. 1600). In firearms, the part of the mechanism which explodes the charge (1540s, probably so called for its resemblance to a door-latching device), hence figurative phrase lock, stock, and barrel (which add up to the whole firearm) "the whole of something" (1842). Phrase under lock and key attested from early 14c.
lock (n.2)
"tress of hair," Old English locc "lock of hair, curl" (plural loccas), from Proto-Germanic *lukkoz (source also of Old Norse lokkr, Old Saxon, Old Frisian, Dutch lok, Old High German loc, German Locke "lock of hair"), a word of uncertain origin. According to OED, perhaps from a PIE *lugnos- and related to Greek lygos "pliant twig, withe," Lithuanian lugnas "flexible" (see reluctance).
lock (v.)
c. 1300, "to fasten with a lock, shut or confine with a lock." The sense is narrowed from that of Old English lucan "to lock, to close" (class II strong verb; past tense leac, past participle locen), from the same verbal root that yielded lock (n.1). The form is from the noun (perhaps reinforced by Old Norse loka); the old original strong verb survived as dialectal louk, and the strong past participle locken lingered a while, as in Middle English loken love "hidden love, clandestine love" (early 14c.).
The Old English verb is cognate with Old Frisian luka "to close," Old Saxon lukan, Old High German luhhan, Old Norse luka, Gothic galukan. Meaning "to fasten parts together" is from late 14c., originally of armor; of persons, "to embrace closely," from mid-14c. Related: Locked; locking. Locked "securely established" is from early 15c. To lock (someone) in "shut in a place" is from c. 1400. Slang lock horns "fight" is from 1839.